The House of Representatives approved, in two rounds, in the early hours of Friday (7) the basic text of the proposal for Constitutional Amendment (PEC 45), which deals with Tax Reform on Consumption.
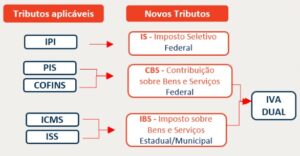
According to the substitute text of PEC 45, and its amendments, presented at the House of Representatives, the reform will begin with the substitution of the taxes levied on consumption (PIS, COFINS, ISS, ICMS and IPI), by the Dual VAT and the Selective Tax (IS). The substitution will take place as follows:
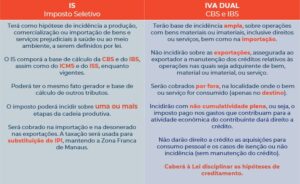
Operation and Basic Characteristics of the new taxes
Important to note
Service Sector and the New Dual VAT
With a few exceptions such as education and health services, medicines, and agricultural products, the bill intends to tax all other sectors at the same rate.
It is estimated that the project has the potential to raise taxation on the services sector, since labor expenses will not be creditable.
Transition: How it will work
2026
- CBS at a rate of 0.9% and the IBS at 0.1%;
- The collected value can be compensated with PIS/COFINS, including in the import;
- Eventual credit balance may be compensated with another federal tax or reimbursed; and
- PIS/COFINS are not part of the CBS calculation basis, and vice-versa.
2027
- CBS as per reference rate;
- Extinction of PIS/COFINS, including on imports; and
- Reduction to zero of the IPI tax rate (except ZFM).
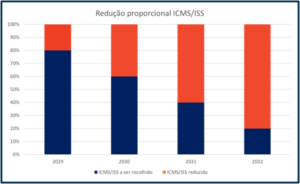
2029 a 2032
- Proportional reduction of the ICMS and ISS rates, as well as tax incentives, according to the schedule on the following slide; and
- ICMS/ISS are not part of the IBS calculation basis and vice-versa.
2033
- Extinction of IPI, ICMS and ISS; and
- CBS and IBS rates calculated by the Federal Audit Court and fixed by Resolution of the Federal Senate.
In practice, during this transition period, there will be an increase in the complexity of compliance with accessory obligations, because the taxpayer will have to meet the requirements of both the current and the new systems.
Changes to other taxes
Tax on Urban Land and Property
- As of the text presented, the municipalities will be able to change the tax calculation basis by decree, but must meet the criteria established by municipal law.
Motor Vehicle Ownership Tax
- In addition to land vehicles, there has been an expansion of the Motor Vehicle Ownership Tax (IPVA) for water and air vehicles;
- The tax rate will depend on the type of vehicle, value, use, and the environmental impact it represents.
Aircraft and vehicles licensed to provide services (air cabs), transport or fishing company vessels, and maritime platforms would be exempt from IPVA.
Causa Mortis Transmission and Donation Tax
- Recognized the possibility of tax progressivity, i.e. higher rates equivalent to the values transmitted or donated.
- There is provision for taxing residents or those domiciled abroad, which depends on a complementary law.
- The competence for taxation of movable property, securities and credits will be of the State of domicile of the deceased.
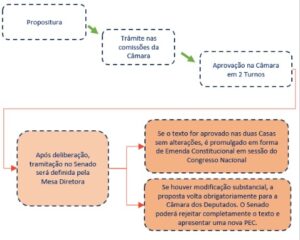
Tax Reform Transition
More information:
Tax Team: tributariocontencioso@btlaw.com.br